CMC injury, or carpometacarpal injury, is a condition that can significantly affect the function of your hand and thumb. This type of injury primarily involves the joint between the wrist and the base of the thumb, which is crucial for gripping and pinching movements. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of CMC injuries, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Understanding this injury is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to ensure effective management and rehabilitation.
With the increasing prevalence of hand injuries related to sports, work, and daily activities, awareness about CMC injury has become more critical than ever. Injuries can range from mild sprains to severe fractures, and accurate diagnosis is vital for effective treatment. The carpometacarpal joint is one of the most mobile joints in the body, which makes it susceptible to various types of injuries, especially in high-impact sports or activities that require repetitive hand movements.
In the following sections, we will explore the intricate details of CMC injuries, helping you understand what leads to them, the signs to look out for, and the best practices for recovery. Whether you're an athlete, a healthcare professional, or simply someone looking to learn more, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into CMC injuries.
Table of Contents
- What is CMC Injury?
- Causes of CMC Injury
- Symptoms of CMC Injury
- Diagnosing CMC Injury
- Treatment Options for CMC Injury
- Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Prevention of CMC Injury
- When to See a Doctor
What is CMC Injury?
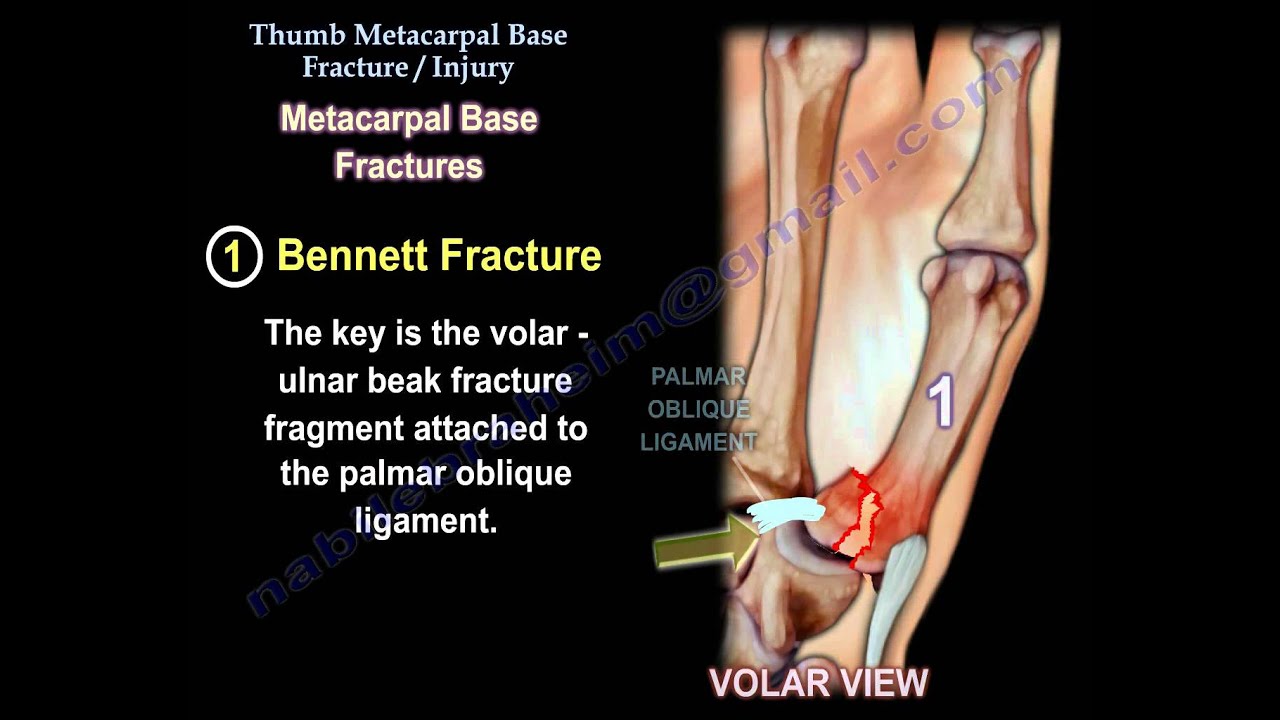
The carpometacarpal joint (CMC) is located at the base of the thumb, where the trapezium bone of the wrist meets the first metacarpal bone. CMC injuries can occur due to a variety of reasons, including trauma, repetitive strain, or degenerative changes. These injuries can significantly impact hand function and lead to pain, swelling, and decreased mobility.
Causes of CMC Injury
CMC injuries can result from a variety of factors, including:
- Trauma: Falls, sports injuries, or accidents can lead to direct trauma to the thumb.
- Repetitive Strain: Activities that involve repetitive gripping or pinching can cause wear and tear on the CMC joint.
- Degenerative Conditions: Arthritis or other degenerative diseases can weaken the joint and make it more prone to injury.
Common Sports Activities Leading to CMC Injury
Several sports are particularly associated with an increased risk of CMC injuries, including:
- Football
- Baseball
- Rock climbing
- Weightlifting
Symptoms of CMC Injury
Individuals with CMC injuries may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Localized pain at the base of the thumb
- Swelling and bruising
- Decreased range of motion
- Difficulty gripping or pinching
Diagnosing CMC Injury
Accurate diagnosis of CMC injuries is crucial for effective treatment. Healthcare providers typically utilize a combination of physical examinations and imaging tests to assess the injury. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination to assess pain, swelling, and mobility.
- X-rays: Imaging to detect fractures or misalignments.
- MRI: Advanced imaging to evaluate soft tissue injuries or degenerative changes.
Treatment Options for CMC Injury
Treatment for CMC injuries varies depending on the severity of the injury. Options may include:
- Conservative Management: Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises to restore mobility and strength.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged ligaments or bones.
Rehabilitation Techniques
Rehabilitation can include a variety of techniques, such as:
- Strengthening exercises
- Range of motion exercises
- Utilization of splints or braces
Rehabilitation and Recovery
The road to recovery from a CMC injury can be lengthy but is essential for regaining full hand function. Following a structured rehabilitation program can help patients return to their normal activities more quickly and safely.
Prevention of CMC Injury
Preventing CMC injuries involves a combination of proper technique and conditioning. Here are some strategies to reduce risk:
- Warming up before physical activities
- Using proper equipment and techniques in sports
- Incorporating strength training for the hands and wrists
When to See a Doctor
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, swelling, or inability to move your thumb after an injury. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and promote better outcomes.
Conclusion
CMC injury can have a significant impact on hand function and quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this injury is crucial for effective management. If you suspect you may have a CMC injury, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
We encourage readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and engage in discussions in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more information on hand injuries and treatments.
Penutup
Thank you for taking the time to read about CMC injury. We hope this article has provided valuable insights and encourages you to return for more informative content in the future. Your health and well-being are important to us!